Automations ¶
Automations in Prefect Cloud enable you to configure actions that Prefect executes automatically based on trigger conditions.
Potential triggers include the occurrence of events from changes in a flow run's state - or the absence of such events. You can even define your own custom trigger to fire based on an event created from a webhook or a custom event defined in Python code.
Potential actions include kicking off flow runs, pausing schedules, and sending custom notifications.
Automations are only available in Prefect Cloud
Notifications in an open-source Prefect server provide a subset of the notification message-sending features available in Automations.
Automations provide a flexible and powerful framework for automatically taking action in response to events.
Automations overview¶
The Automations page provides an overview of all configured automations for your workspace.
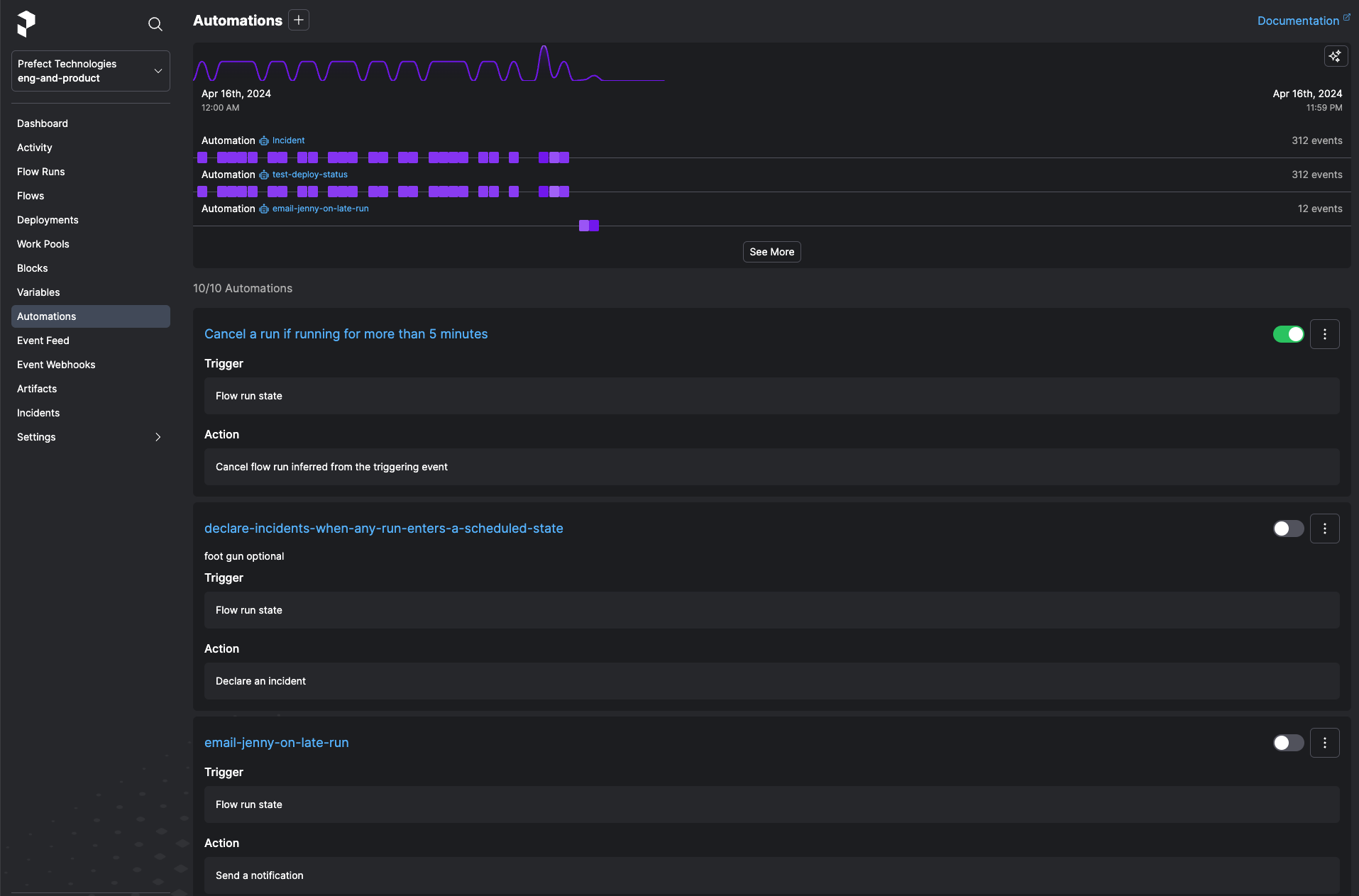
Selecting the toggle next to an automation pauses execution of the automation.
The button next to the toggle provides commands to copy the automation ID, edit the automation, or delete the automation.
Select the name of an automation to view Details about it and relevant Events.
Create an automation¶
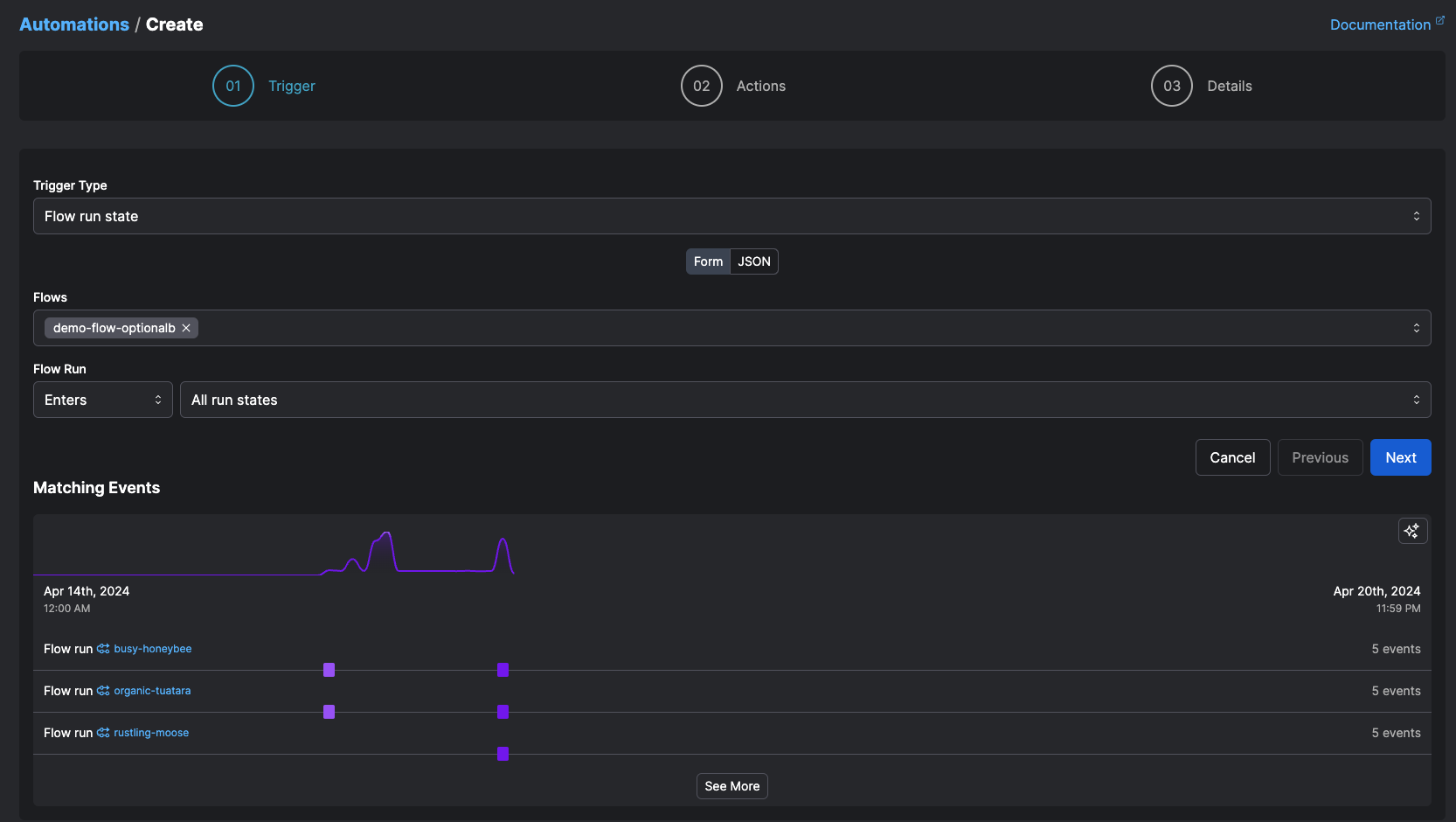
On the Automations page, select the + icon to create a new automation. You'll be prompted to configure:
- A trigger condition that causes the automation to execute.
- One or more actions carried out by the automation.
- Details about the automation, such as a name and description.
Triggers¶
Triggers specify the conditions under which your action should be performed. The Prefect UI includes templates for many common conditions, such as:
- Flow run state change
- Note - Flow Run Tags currently are only evaluated with
ORcriteria - Work pool status
- Work queue status
- Deployment status
- Metric thresholds, such as average duration, lateness, or completion percentage
- Incident declarations (available on Pro and Custom plans)
- Custom event triggers
Automations API
The automations API enables further programmatic customization of trigger and action policies based on arbitrary events.
Importantly, triggers can be configured not only in reaction to events, but also proactively: to fire in the absence of an expected event.
For example, in the case of flow run state change triggers, you might expect production flows to finish in no longer than thirty minutes. But transient infrastructure or network issues could cause your flow to get “stuck” in a running state. A trigger could kick off an action if the flow stays in a running state for more than 30 minutes. This action could be taken on the flow itself, such as canceling or restarting it. Or the action could take the form of a notification so someone can take manual remediation steps. Or you could set both actions to to take place when the trigger occurs.
Actions¶
Actions specify what your automation does when its trigger criteria are met. Current action types include:
- Cancel a flow run
- Pause or resume a schedule
- Run a deployment
- Pause or resume a deployment schedule
- Pause or resume a work pool
- Pause or resume a work queue
- Pause or resume an automation
- Send a notification
- Call a webhook
- Suspend a flow run
- Declare an incident (available on Pro and Custom plans)
- Change the state of a flow run
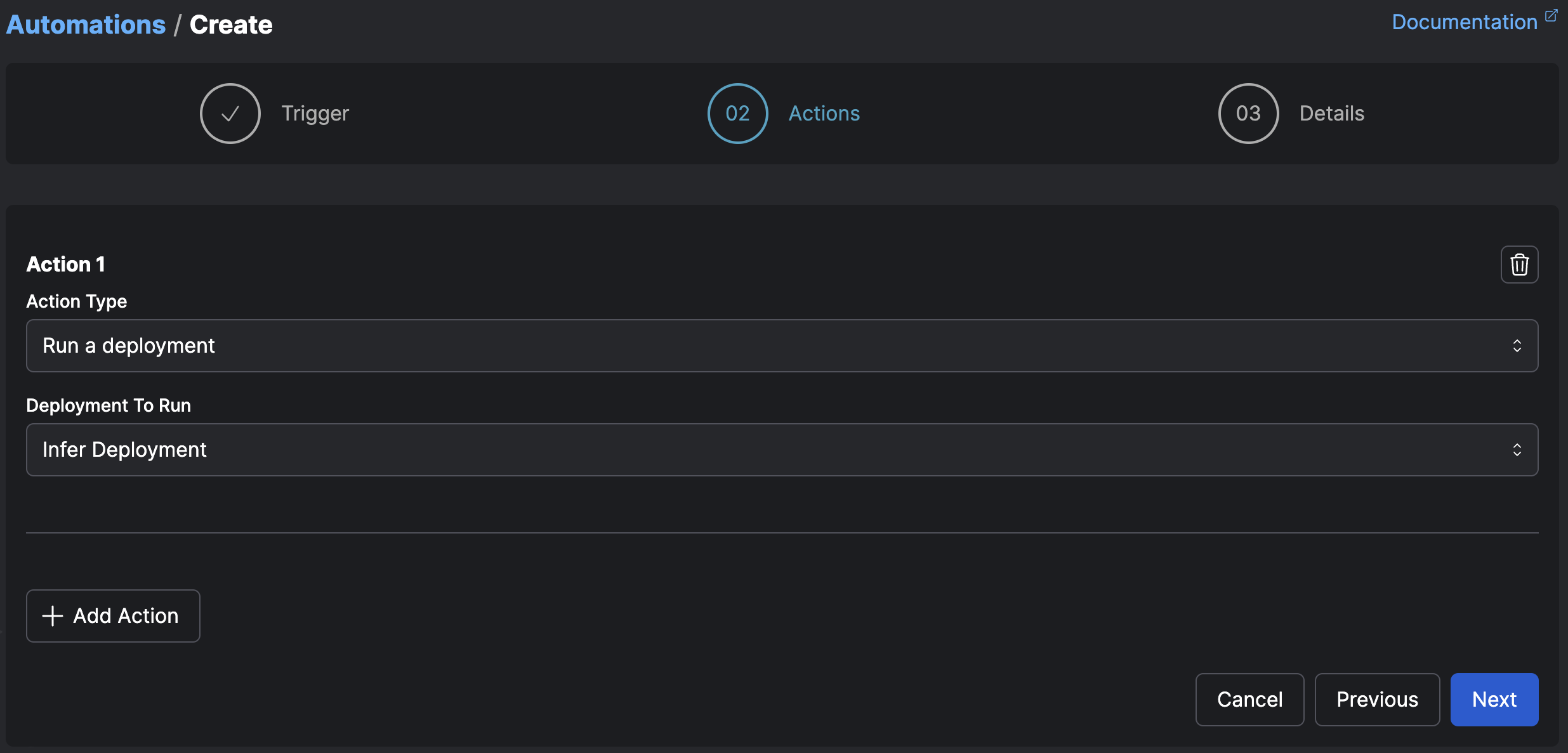
Selected and inferred action targets¶
Some actions require you to either select the target of the action, or specify that the target of the action should be inferred.
Selected targets are simple, and useful for when you know exactly what object your action should act on — for example, the case of a cleanup flow you want to run or a specific notification you’d like to send.
Inferred targets are deduced from the trigger itself.
For example, if a trigger fires on a flow run that is stuck in a running state, and the action is to cancel an inferred flow run, the flow run to cancel is inferred as the stuck run that caused the trigger to fire.
Similarly, if a trigger fires on a work queue event and the corresponding action is to pause an inferred work queue, the inferred work queue is the one that emitted the event.
Prefect tries to infer the relevant event whenever possible, but sometimes one does not exist.
Specify a name and, optionally, a description for the automation.
Custom triggers¶
When you need a trigger that doesn't quite fit the templates in UI trigger builder, you can define a custom trigger in JSON. With custom triggers, you have access to the full capabilities of Prefect's automation system - allowing you to react to many kinds of events and metrics in your workspace.
Each automation has a single trigger that, when fired, will cause all of its associated actions to run. That single trigger may be a reactive or proactive event trigger, a trigger monitoring the value of a metric, or a composite trigger that combines several underlying triggers.
Event triggers¶
Event triggers are the most common types of trigger, and they are intended to react to the presence or absence of an event happening in your workspace. Event triggers are indicated with {"type": "event"}.
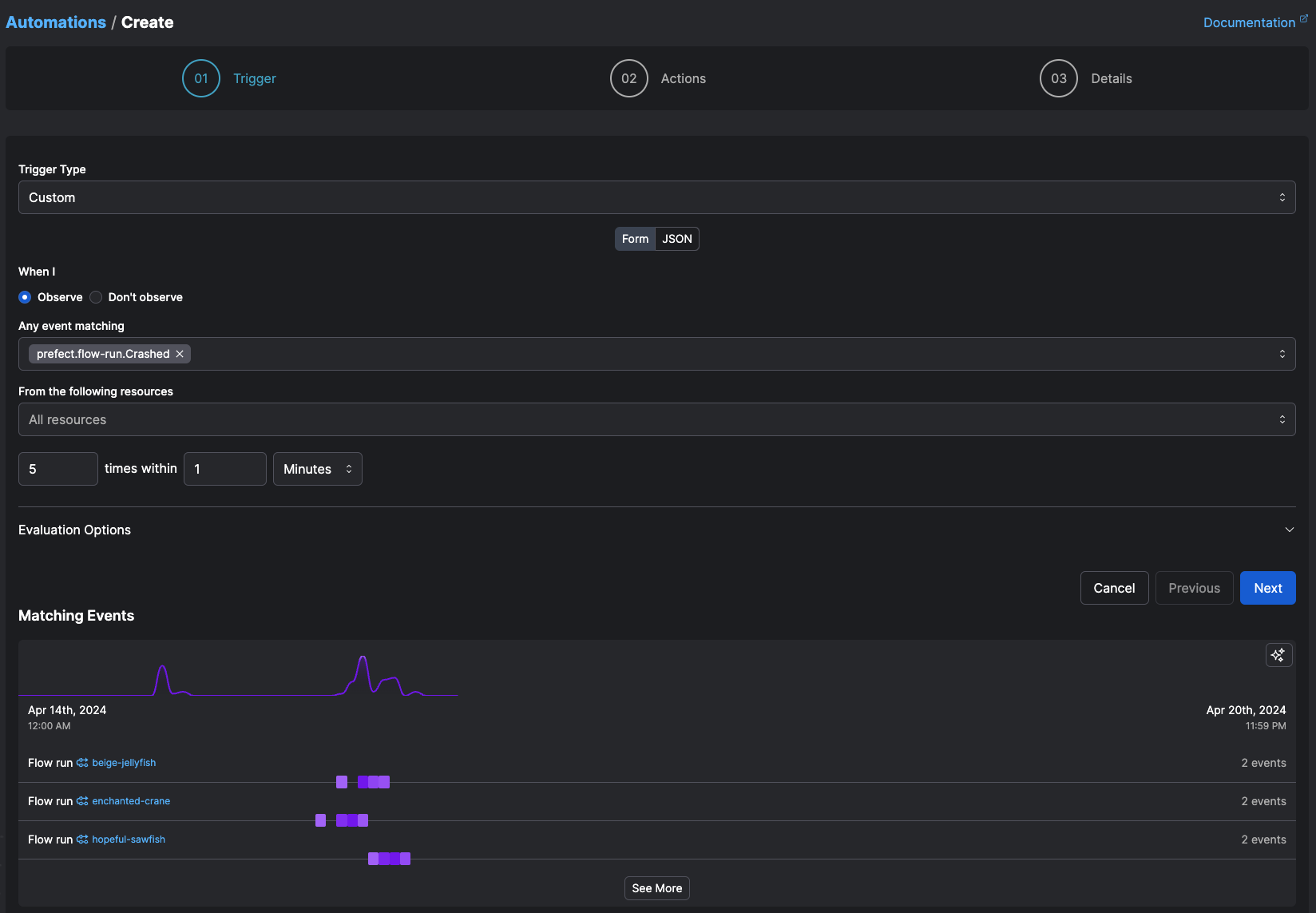
The schema that defines an event trigger is as follows:
| Name | Type | Supports trailing wildcards | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| match | object | Labels for resources which this Automation will match. | |
| match_related | object | Labels for related resources which this Automation will match. | |
| posture | string enum | N/A | The posture of this Automation, either Reactive or Proactive. Reactive automations respond to the presence of the expected events, while Proactive automations respond to the absence of those expected events. |
| after | array of strings | Event(s), one of which must have first been seen to start this automation. | |
| expect | array of strings | The event(s) this automation is expecting to see. If empty, this automation will evaluate any matched event. | |
| for_each | array of strings | Evaluate the Automation separately for each distinct value of these labels on the resource. By default, labels refer to the primary resource of the triggering event. You may also refer to labels from related resources by specifying related:<role>:<label>. This will use the value of that label for the first related resource in that role. |
|
| threshold | integer | N/A | The number of events required for this Automation to trigger (for Reactive automations), or the number of events expected (for Proactive automations) |
| within | number | N/A | The time period over which the events must occur. For Reactive triggers, this may be as low as 0 seconds, but must be at least 10 seconds for Proactive triggers |
Resource matching¶
Both the event and metric triggers support matching events for specific resources in your workspace, including most Prefect objects (like flows, deployment, blocks, work pools, tags, etc) as well as resources you have defined in any events you emit yourself. The match and match_related fields control which events a trigger considers for evaluation by filtering on the contents of their resource and related fields, respectively. Each label added to a match filter is ANDed with the other labels, and can accept a single value or a list of multiple values that are ORed together.
Consider the resource and related fields on the following prefect.flow-run.Completed event, truncated for the sake of example. Its primary resource is a flow run, and since that flow run was started via a deployment, it is related to both its flow and its deployment:
"resource": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.flow-run.925eacce-7fe5-4753-8f02-77f1511543db",
"prefect.resource.name": "cute-kittiwake"
}
"related": [
{
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.flow.cb6126db-d528-402f-b439-96637187a8ca",
"prefect.resource.role": "flow",
"prefect.resource.name": "hello"
},
{
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.deployment.37ca4a08-e2d9-4628-a310-cc15a323378e",
"prefect.resource.role": "deployment",
"prefect.resource.name": "example"
}
]
There are a number of valid ways to select the above event for evaluation, and the approach depends on the purpose of the automation.
The following configuration will filter for any events whose primary resource is a flow run, and that flow run has a name starting with cute- or radical-.
"match": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.flow-run.*",
"prefect.resource.name": ["cute-*", "radical-*"]
},
"match_related": {},
...
This configuration, on the other hand, will filter for any events for which this specific deployment is a related resource.
"match": {},
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.deployment.37ca4a08-e2d9-4628-a310-cc15a323378e"
},
...
Both of the above approaches will select the example prefect.flow-run.Completed event, but will permit additional, possibly undesired events through the filter as well. match and match_related can be combined for more restrictive filtering:
"match": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.flow-run.*",
"prefect.resource.name": ["cute-*", "radical-*"]
},
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.deployment.37ca4a08-e2d9-4628-a310-cc15a323378e"
},
...
Now this trigger will filter only for events whose primary resource is a flow run started by a specific deployment, and that flow run has a name starting with cute- or radical-.
Expected events¶
Once an event has passed through the match filters, it must be decided if this event should be counted toward the trigger's threshold. Whether that is the case is determined by the event names present in expect.
This configuration informs the trigger to evaluate only prefect.flow-run.Completed events that have passed the match filters.
"expect": [
"prefect.flow-run.Completed"
],
...
threshold decides the quantity of expected events needed to satisfy the trigger. Increasing the threshold above 1 will also require use of within to define a range of time in which multiple events are seen. The following configuration will expect two occurrences of prefect.flow-run.Completed within 60 seconds.
"expect": [
"prefect.flow-run.Completed"
],
"threshold": 2,
"within": 60,
...
after can be used to handle scenarios that require more complex event reactivity.
Take, for example, this flow which emits an event indicating the table it operates on is missing or empty:
from prefect import flow
from prefect.events import emit_event
from db import Table
@flow
def transform(table_name: str):
table = Table(table_name)
if not table.exists():
emit_event(
event="table-missing",
resource={"prefect.resource.id": "etl-events.transform"}
)
elif table.is_empty():
emit_event(
event="table-empty",
resource={"prefect.resource.id": "etl-events.transform"}
)
else:
# transform data
The following configuration uses after to prevent this automation from firing unless either a table-missing or a table-empty event has occurred before a flow run of this deployment completes.
Tip
Note how match and match_related are used to ensure the trigger only evaluates events that are relevant to its purpose.
"match": {
"prefect.resource.id": [
"prefect.flow-run.*",
"etl-events.transform"
]
},
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.deployment.37ca4a08-e2d9-4628-a310-cc15a323378e"
}
"after": [
"table-missing",
"table-empty"
]
"expect": [
"prefect.flow-run.Completed"
],
...
Evaluation strategy¶
All of the previous examples were designed around a reactive posture - that is, count up events toward the threshold until it is met, then execute actions. To respond to the absence of events, use a proactive posture. A proactive trigger will fire when its threshold has not been met by the end of the window of time defined by within. Proactive triggers must have a within value of at least 10 seconds.
The following trigger will fire if a prefect.flow-run.Completed event is not seen within 60 seconds after a prefect.flow-run.Running event is seen.
{
"match": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.flow-run.*"
},
"match_related": {},
"after": [
"prefect.flow-run.Running"
],
"expect": [
"prefect.flow-run.Completed"
],
"for_each": [],
"posture": "Proactive",
"threshold": 1,
"within": 60
}
However, without for_each, a prefect.flow-run.Completed event from a different flow run than the one that started this trigger with its prefect.flow-run.Running event could satisfy the condition. Adding a for_each of prefect.resource.id will cause this trigger to be evaluated separately for each flow run id associated with these events.
{
"match": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.flow-run.*"
},
"match_related": {},
"after": [
"prefect.flow-run.Running"
],
"expect": [
"prefect.flow-run.Completed"
],
"for_each": [
"prefect.resource.id"
],
"posture": "Proactive",
"threshold": 1,
"within": 60
}
Metric triggers¶
Metric triggers ({"type": "metric"}) fire when the value of a metric in your workspace crosses a threshold you've defined. For example, you can trigger an automation when the success rate of flows in your workspace drops below 95% over the course of an hour.
Prefect's metrics are all derived by examining your workspace's events, and if applicable, use the occurred times of those events as the basis for their calculations.
Prefect defines three metrics today:
- Successes (
{"name": "successes"}), defined as the number of flow runs that wentPendingand then the latest state we saw was not a failure (FailedorCrashed). This metric accounts for retries if the ultimate state was successful. - Duration (
{"name": "duration"}), defined as the length of time that a flow remains in aRunningstate before transitioning to a terminal state such asCompleted,Failed, orCrashed. Because this time is derived in terms of flow run state change events, it may be greater than the runtime of your function. - Lateness (
{"name": "lateness"}), defined as the length of time that aScheduledflow remains in aLatestate before transitioning to aRunningand/orCrashedstate. Only flow runs that the system marksLateare included.
The schema of a metric trigger is as follows:
| Name | Type | Supports trailing wildcards | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| match | object | Labels for resources which this Automation will match. | |
| match_related | object | Labels for related resources which this Automation will match. | |
| metric | MetricTriggerQuery |
N/A | The definition of the metric query to run |
And the MetricTriggerQuery query is defined as:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | string | The name of the Prefect metric to evaluate (see above). |
| threshold | number | The threshold to which the current metric value is compared |
| operator | string ("<", "<=", ">", ">=") |
The comparison operator to use to decide if the threshold value is met |
| range | duration in seconds | How far back to evaluate the metric |
| firing_for | duration in seconds | How long the value must exceed the threshold before this trigger fires |
For example, to fire when flow runs tagged production in your workspace are failing at a rate of 10% or worse for the last hour (in other words, your success rate is below 90%), create this trigger:
{
"type": "metric",
"match": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.flow-run.*"
},
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.tag.production",
"prefect.resource.role": "tag"
},
"metric": {
"name": "successes",
"threshold": 0.9,
"operator": "<",
"range": 3600,
"firing_for": 0
}
}
To detect when the average lateness of your Kubernetes workloads (running on a work pool named kubernetes) in the last day exceeds 5 minutes late, and that number hasn't gotten better for the last 10 minutes, use a trigger like this:
{
"type": "metric",
"match": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.flow-run.*"
},
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.work-pool.kubernetes",
"prefect.resource.role": "work-pool"
},
"metric": {
"name": "lateness",
"threshold": 300,
"operator": ">",
"range": 86400,
"firing_for": 600
}
}
Composite triggers¶
To create a trigger from multiple kinds of events and metrics, use a compound or sequence trigger. These higher-order triggers are composed from a set of underlying event and metric triggers.
For example, if you want to run a deployment only after three different flows in your workspace have written their results to a remote filesystem, combine them with a 'compound' trigger:
{
"type": "compound",
"require": "all",
"within": 3600,
"triggers": [
{
"type": "event",
"posture": "Reactive",
"expect": ["prefect.block.remote-file-system.write_path.called"],
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.name": "daily-customer-export",
"prefect.resource.role": "flow"
}
},
{
"type": "event",
"posture": "Reactive",
"expect": ["prefect.block.remote-file-system.write_path.called"],
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.name": "daily-revenue-export",
"prefect.resource.role": "flow"
}
},
{
"type": "event",
"posture": "Reactive",
"expect": ["prefect.block.remote-file-system.write_path.called"],
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.name": "daily-expenses-export",
"prefect.resource.role": "flow"
}
}
]
}
This trigger will fire once it sees at least one of each of the underlying event triggers fire within the time frame specified. Then the trigger will reset its state and fire the next time these three events all happen. The order the events occur doesn't matter, just that all of the events occur within one hour.
If you want a flow run to complete prior to starting to watch for those three events, you can combine the entire previous trigger as the second part of a sequence of two triggers:
{
// the outer trigger is now a "sequence" trigger
"type": "sequence",
"within": 7200,
"triggers": [
// with the first child trigger expecting a Completed event
{
"type": "event",
"posture": "Reactive",
"expect": ["prefect.flow-run.Completed"],
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.name": "daily-export-initiator",
"prefect.resource.role": "flow"
}
},
// and the second child trigger being the compound trigger from the prior example
{
"type": "compound",
"require": "all",
"within": 3600,
"triggers": [
{
"type": "event",
"posture": "Reactive",
"expect": ["prefect.block.remote-file-system.write_path.called"],
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.name": "daily-customer-export",
"prefect.resource.role": "flow"
}
},
{
"type": "event",
"posture": "Reactive",
"expect": ["prefect.block.remote-file-system.write_path.called"],
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.name": "daily-revenue-export",
"prefect.resource.role": "flow"
}
},
{
"type": "event",
"posture": "Reactive",
"expect": ["prefect.block.remote-file-system.write_path.called"],
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.name": "daily-expenses-export",
"prefect.resource.role": "flow"
}
}
]
}
]
}
In this case, the trigger will only fire if it sees the daily-export-initiator flow complete, and then the three files written by the other flows.
The within parameter for compound and sequence triggers constrains how close in time (in seconds) the child triggers must fire to satisfy the composite trigger. For example, if the daily-export-initiator flow runs, but the other three flows don't write their result files until three hours later, this trigger won't fire. Placing these time constraints on the triggers can prevent a misfire if you know that the events will generally happen within a specific timeframe, and you don't want a stray older event to be included in the evaluation of the trigger. If this isn't a concern for you, you may omit the within period, in which case there is no limit to how far apart in time the child triggers occur.
Any type of trigger may be composed into higher-order composite triggers, including proactive event triggers and metric triggers. In the following example, the compound trigger will fire if any of the following events occur: a flow run stuck in Pending, a work pool becoming unready, or the average amount of Late work in your workspace going over 10 minutes:
{
"type": "compound",
"require": "any",
"triggers": [
{
"type": "event",
"posture": "Proactive",
"after": ["prefect.flow-run.Pending"],
"expect": ["prefect.flow-run.Running", "prefect.flow-run.Crashed"],
"for_each": ["prefect.resource.id"],
"match_related": {
"prefect.resource.name": "daily-customer-export",
"prefect.resource.role": "flow"
}
},
{
"type": "event",
"posture": "Reactive",
"expect": ["prefect.work-pool.not_ready"],
"match": {
"prefect.resource.name": "kubernetes-workers",
}
},
{
"type": "metric",
"metric": {
"name": "lateness",
"operator": ">",
"threshold": 600,
"range": 3600,
"firing_for": 300
}
}
]
}
For compound triggers, the require parameter may be "any", "all", or a number between 1 and the number of child triggers. In the example above, if you feel that you are receiving too many spurious notifications for issues that resolve on their own, you can specify {"require": 2} to express that any two of the triggers must fire in order for the compound trigger to fire. Sequence triggers, on the other hand, always require all of their child triggers to fire before they fire.
Compound triggers are defined as:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| require | number, "any", or "all" |
How many of the child triggers must fire for this trigger to fire |
| within | time, in seconds | How close in time the child triggers must fire for this trigger to fire |
| triggers | array of other triggers |
Sequence triggers are defined as:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| within | time, in seconds | How close in time the child triggers must fire for this trigger to fire |
| triggers | array of other triggers |
Create an automation via deployment triggers¶
To enable the simple configuration of event-driven deployments, Prefect provides deployment triggers - a shorthand for creating automations that are linked to specific deployments to run them based on the presence or absence of events.
# prefect.yaml
deployments:
- name: my-deployment
entrypoint: path/to/flow.py:decorated_fn
work_pool:
name: my-process-pool
triggers:
- enabled: true
match:
prefect.resource.id: my.external.resource
expect:
- external.resource.pinged
parameters:
param_1: "{{ event }}"
At deployment time, this will create a linked automation that is triggered by events matching your chosen grammar, which will pass the templatable event as a parameter to the deployment's flow run.
Pass triggers to prefect deploy¶
You can pass one or more --trigger arguments to prefect deploy, which can be either a JSON string or a path to a .yaml or .json file.
# Pass a trigger as a JSON string
prefect deploy -n test-deployment \
--trigger '{
"enabled": true,
"match": {
"prefect.resource.id": "prefect.flow-run.*"
},
"expect": ["prefect.flow-run.Completed"]
}'
# Pass a trigger using a JSON/YAML file
prefect deploy -n test-deployment --trigger triggers.yaml
prefect deploy -n test-deployment --trigger my_stuff/triggers.json
For example, a triggers.yaml file could have many triggers defined:
triggers:
- enabled: true
match:
prefect.resource.id: my.external.resource
expect:
- external.resource.pinged
parameters:
param_1: "{{ event }}"
- enabled: true
match:
prefect.resource.id: my.other.external.resource
expect:
- some.other.event
parameters:
param_1: "{{ event }}"
Both of the above triggers would be attached to test-deployment after running prefect deploy.
Triggers passed to prefect deploy will override any triggers defined in prefect.yaml
While you can define triggers in prefect.yaml for a given deployment, triggers passed to prefect deploy will
take precedence over those defined in prefect.yaml.
Note that deployment triggers contribute to the total number of automations in your workspace.
Automation notifications¶
Notifications enable you to set up automation actions that send a message.
Automation notifications support sending notifications via any predefined block that is capable of and configured to send a message. That includes, for example:
- Slack message to a channel
- Microsoft Teams message to a channel
- Email to a configured email address
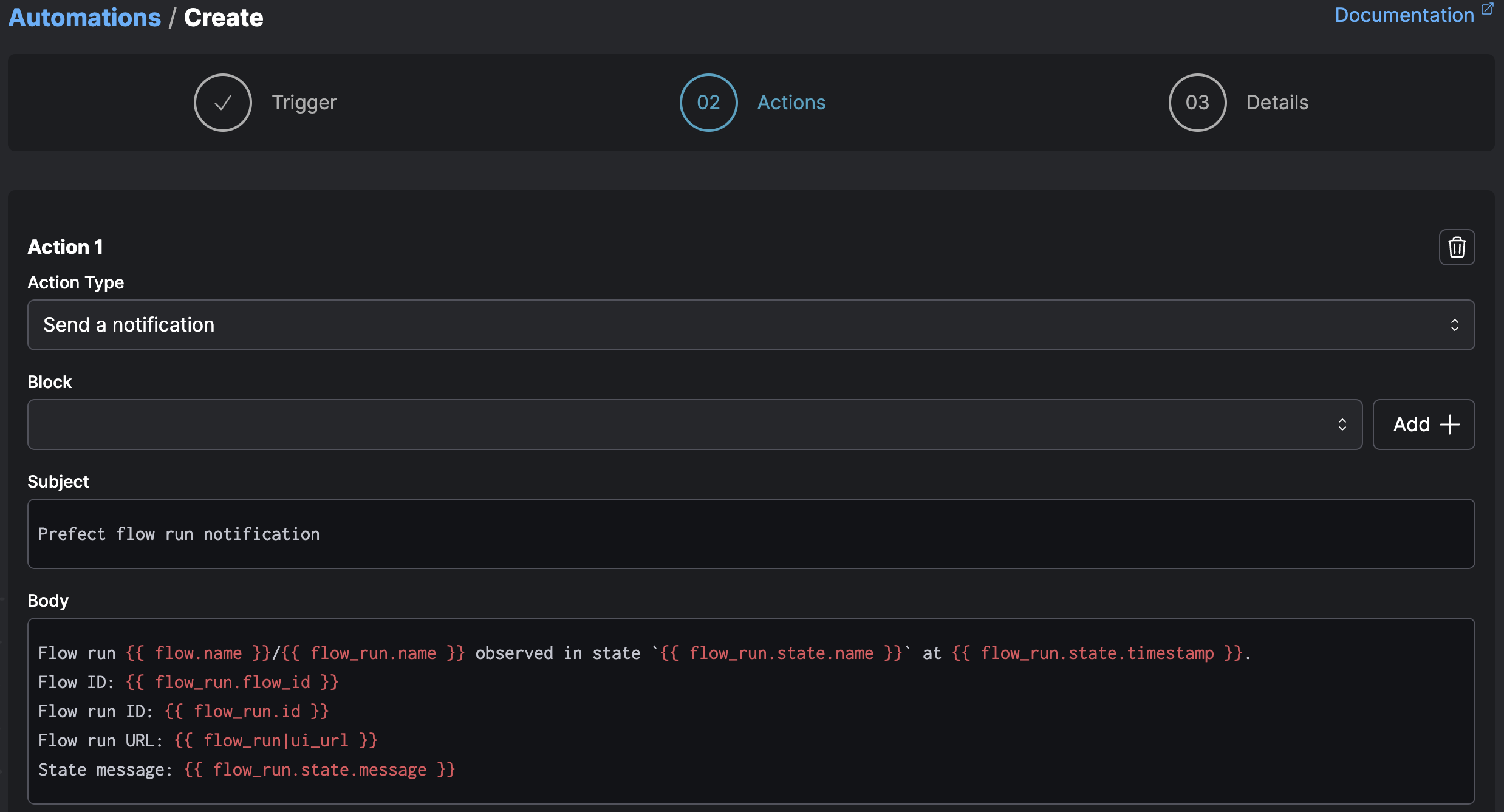
Templating with Jinja¶
Automation actions can access templated variables through Jinja syntax. Templated variables enable you to dynamically include details from an automation trigger, such as a flow or pool name.
Jinja templated variable syntax wraps the variable name in double curly brackets, like this: {{ variable }}.
You can access properties of the underlying flow run objects including:
In addition to its native properties, each object includes an id along with created and updated timestamps.
The flow_run|ui_url token returns the URL for viewing the flow run in Prefect Cloud.
Here’s an example for something that would be relevant to a flow run state-based notification:
Flow run {{ flow_run.name }} entered state {{ flow_run.state.name }}.
Timestamp: {{ flow_run.state.timestamp }}
Flow ID: {{ flow_run.flow_id }}
Flow Run ID: {{ flow_run.id }}
State message: {{ flow_run.state.message }}
The resulting Slack webhook notification would look something like this:
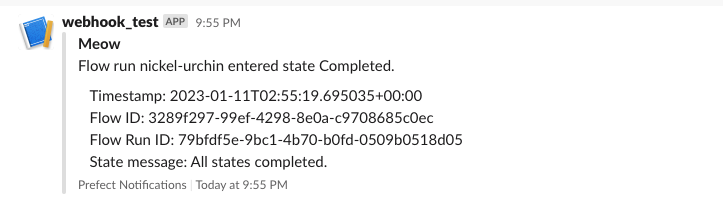
You could include flow and deployment properties.
Flow run {{ flow_run.name }} for flow {{ flow.name }}
entered state {{ flow_run.state.name }}
with message {{ flow_run.state.message }}
Flow tags: {{ flow_run.tags }}
Deployment name: {{ deployment.name }}
Deployment version: {{ deployment.version }}
Deployment parameters: {{ deployment.parameters }}
An automation that reports on work pool status might include notifications using work_pool properties.
Work pool status alert!
Name: {{ work_pool.name }}
Last polled: {{ work_pool.last_polled }}
In addition to those shortcuts for flows, deployments, and work pools, you have access to the automation and the event that triggered the automation. See the Automations API for additional details.
Automation: {{ automation.name }}
Description: {{ automation.description }}
Event: {{ event.id }}
Resource:
{% for label, value in event.resource %}
{{ label }}: {{ value }}
{% endfor %}
Related Resources:
{% for related in event.related %}
Role: {{ related.role }}
{% for label, value in event.resource %}
{{ label }}: {{ value }}
{% endfor %}
{% endfor %}
Note that this example also illustrates the ability to use Jinja features such as iterator and for loop control structures when templating notifications.